Unleashing Tech Power: Your Shield Against Cold and Flu Battles!

With the onset of the cold and flu season, people everywhere start to take precautions to prevent and treat these illnesses. While traditional methods like vaccination, frequent hand washing, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are crucial, recent years have seen an increase in the utilization of safety technology to further combat the spread of these infectious diseases. This blog post delves into the innovative ways safety technology is playing a pivotal role in this fight.
1. Wearable Health Monitors
Wearables, like smartwatches and fitness bands, have now advanced beyond mere step counting. They can monitor vital signs such as heart rate, body temperature, and even detect changes in your body's biochemistry. If there's a sudden spike in temperature or irregular heart rhythms, wearables can give early warnings, prompting individuals to seek medical advice or self-isolate, reducing the spread of colds and flu.
2. UV-C Sanitizing Devices
Ultraviolet (UV-C) light has been shown to effectively kill viruses, including the cold and flu. Portable UV-C sanitizing devices are now available for consumers, allowing them to disinfect everyday items such as phones, keys, and other personal belongings. While these should not replace traditional cleaning methods, they can serve as an additional layer of protection.
3. Air Purifiers with HEPA Filters
High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters can trap harmful particles as small as 0.3 microns. This makes them effective at capturing the droplets that carry cold and flu viruses. Using air purifiers equipped with HEPA filters in public spaces and homes can reduce the airborne transmission of these illnesses.
4. Contactless Operations
While the common cold and flu are primarily transmitted through respiratory droplets, there's still a risk of transmission through contaminated surfaces. Contactless document options, touchfree doors, and sensor-operated sinks and hand sanitizers can help reduce the need to touch surfaces, limiting potential spread.
5. Telemedicine Platforms
Avoiding crowded places, especially when you're feeling under the weather, can help reduce the spread of cold and flu. Telemedicine platforms have risen in popularity, allowing patients to consult doctors virtually, receive prescriptions, and even get mental health support, all without leaving their homes.
6. AI-Powered Predictive Analysis
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being employed to predict outbreaks and transmission patterns of various diseases, including colds and flu. By analyzing vast amounts of data, these systems can offer early warnings to healthcare institutions and the general public, allowing them to be better prepared.
7. Smart Thermometers
These aren't your average thermometers. Smart thermometers can sync data to an app, allowing users to track their temperature over time, and even receive advice based on the readings. Some platforms aggregate anonymous data to monitor potential outbreaks in realtime, giving communities an advanced heads-up of potential disease spread.
Conclusion
Safety technology has significantly expanded our arsenal in combating the spread of colds and flu. By integrating these technologies into our daily lives and traditional prevention methods, we can better shield ourselves and our communities from the seasonal onslaught of these illnesses. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovations that prioritize our health and well-being.
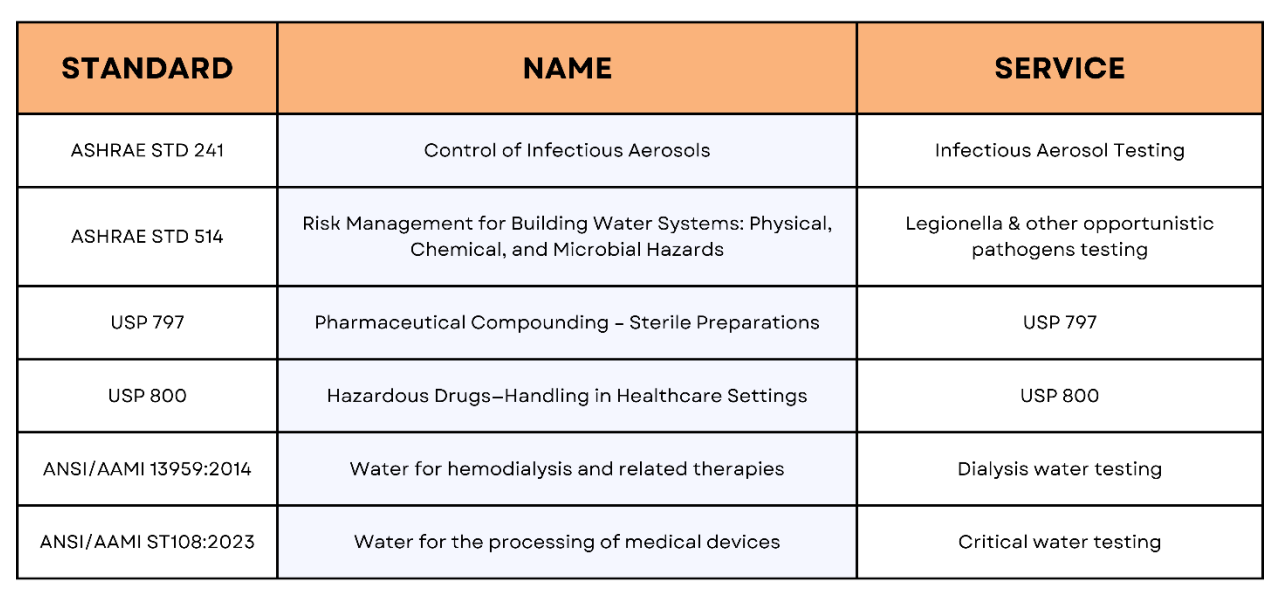
At SEA, we understand the critical role that clean air and clean surfaces plays in this fight and with several new health building standards on the horizon it is time to start preparing.
Our specialized Indoor Air Quality Studies can help identify potential problem areas in your environment. Plus, with our advanced virus and bacteria decontamination services, you can ensure a safer, cleaner space for all. Trust in SEA: where innovation meets health, ensuring a brighter, healthier tomorrow.
By Derek Jennings, President Safety & Environmental Associates (SEA) Inc.