Blog Layout
OSHA REQUIREMENTS FOR SMALL BUSINESSES – WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW

The Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA) is a division of the United States Department of Labor. OSHA was created in 1971 to administer the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970. The act established a nationwide program to protect workers from injury, illness, and death caused by unsafe working conditions. Small businesses are required to comply with OSHA regulations.
Abiding by OSHA laws is not only required, it makes smart business sense. Employees who become ill or are injured due to unsafe working conditions are costly. Reductions in staff morale, decreased productivity, significant costs, and high turnover are often direct results of inadequate attention to the quality of the workplace.
Getting Started
OSHA and small businesses share the responsibility when it comes to fostering a healthy and safe place in which to work. It is essential that you become knowledgeable about the specific OSHA regulations that apply to your business. Not knowing may result in worker injury, hefty fines, and severe penalties. Due to the diversity of small business fields, the complexities of OSHA requirements, and the potential fines and penalties for non-compliance, you may be asking yourself, “Where do I start?”
Enrollment in industry-specific OSHA training classes is a cost-effective, proven method of learning about what is required. The right training program begins with an assessment of your business. The finest OSHA training classes give business owners, managers and staff the tools to work within in the law and improve their respective working conditions.
SEA Inc. is a leader in OSHA compliance education. With emphasis on customized training, SEA Inc. offers powerful compliance programs that go beyond teaching regulations. Conducted in a classroom environment, either on-site or at a training facility, knowledgeable and experienced instructors guide students through a hands-on experience that meets or exceeds OSHA requirements.
Planning and Training for the Proposed Changes
Although EPA is already planning webinars to help bring NPDES organizations up to speed with the new rule, the experts at SET believe that hands-on training offers a far better option for those NPDES-permitted municipalities, businesses and industries that must make changes to meet the new reporting requirements. That is why SET offers comprehensive training, planning and consulting, not only for NPDES compliance but for such programs as Hazardous Waste Management, RCRA Compliance, DOT, SPCC, and Hazardous Materials Management as well. SET training instructors have updated industry knowledge and the ability to convey that information in an understandable format to managers and workers who deal with the handling and disposal of hazardous materials or industrial waste.
OSHA 10 Training
OSHA 10 training from SEA Inc. is a one-of-a-kind program, designed to take students step-by-step through OSHA regulations tailored to their business needs. The OSHA Ten Hour training course covers all aspects of navigating through the often-confusing ocean of OSHA requirements. Business leaders learn to protect employees, fill out reports, and communicate with OSHA representatives. In addition, they learn about the most common industry fines and violations and how to avoid them.
The OSHA Ten Hour training course assists business professionals in engaging each employee in the safety compliance process. Involved employees are more likely to work within the rules and avoid mistakes.
SEA Inc. also offers a more comprehensive 30-hour training class, designed to delve even further into the intricacies of working within OSHA regulations.
Avoid Fines and Penalties – Enroll Today
SEA Inc. is comprised of a fully accredited team with over 225 years of combined safety, health, and compliance expertise. Ongoing training and continuing education ensures that instructors stay current about the latest additions and changes to OSHA regulations. Each course is presented in an appealing way that encourages learning and knowledge retention.
SEA Inc. offers affordable OSHA training options designed exclusively for your business. Tailored to your individual needs, SEA Inc. programs provide the detailed instruction and hands-on training that keep you OSHA compliant and increase worker health and safety.
Enrolling is easy. Contact us or call 501-568-3111 or toll free 888-627-8740 to learn how.

By Derek Jennings
•
February 10, 2025
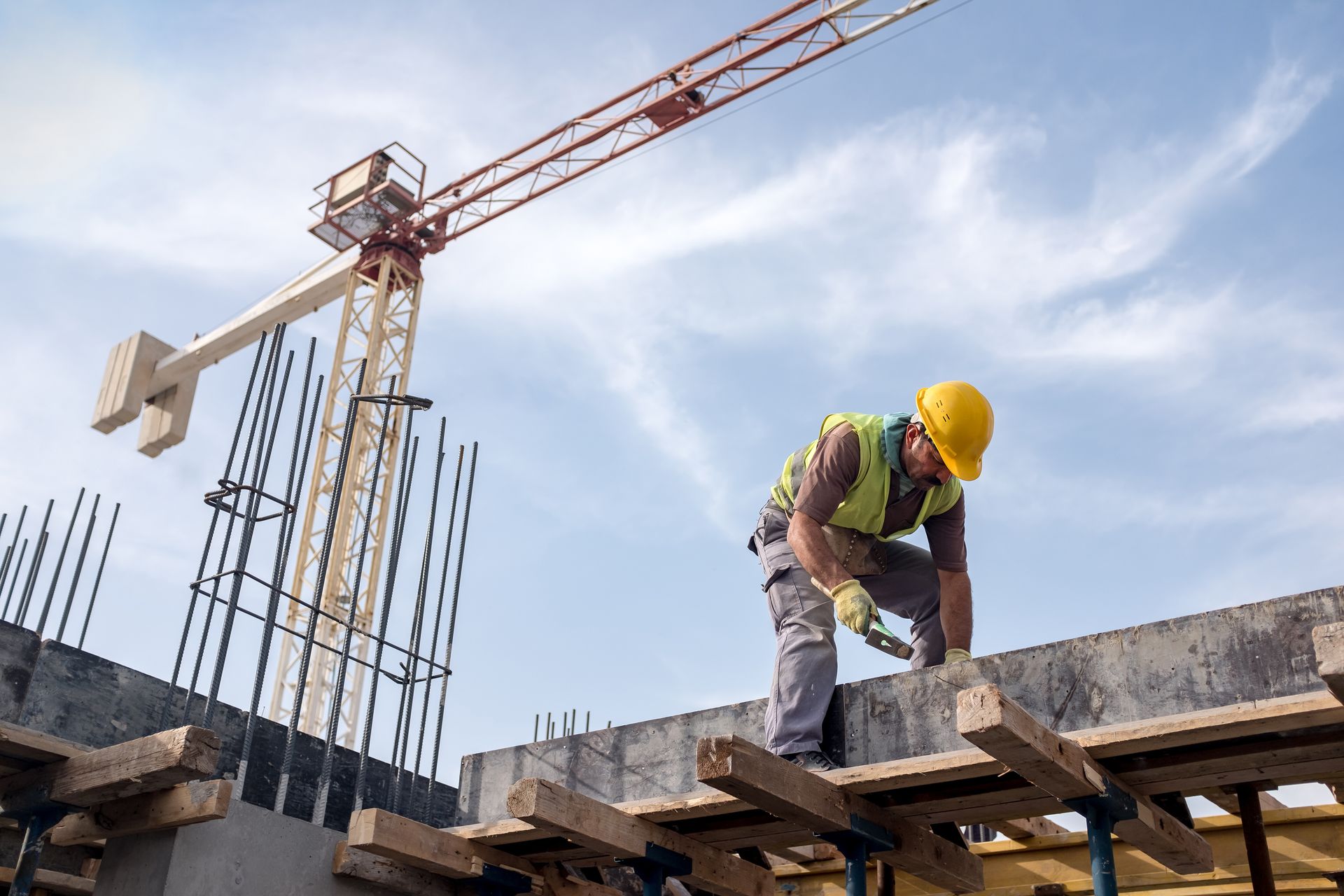
Each year, as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) releases its list of the top 10 workplace safety violations, a pattern emerges that begs a question: Are these frequent violations a sign that employers continue to struggle with the same safety issues, or does it reflect a disposition among OSHA inspectors to focus on areas where they are trained to focus? The Persistent Issue of Repeated Findings The repetition of certain violations year after year might seem surprising, but it underscores a significant challenge in workplace safety management. The top violations tend to be those that are most visible and easiest to spot during inspections, such as fall protection and hazard communication. This consistency suggests that while awareness is high, practical implementation and adherence to safety practices lag behind. Top 10 Most Cited Health and Safety Standards of 2024 1. . Fall Protection, General Requirements: 6,307 violations For the 14th consecutive year, fall protection tops the list of OSHA's enforcement priorities. This emphasis is not arbitrary; OSHA has designated fall protection as a national emphasis area, making it a primary focus during inspections. It's often one of the easiest violations to spot without extensive investigation skills. The OSHA standard 1926.501 mandates that employers must provide fall protection systems like guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems for workers at risk of falls of six feet or more in construction and four feet in general industry. Often, the major factor in these violations is human behavior. Many offenders might think, "No one is watching, and this will only take a moment, so it's no big deal." However, this mindset can lead to non-compliance with critical safety measures, putting worker safety at significant risk.
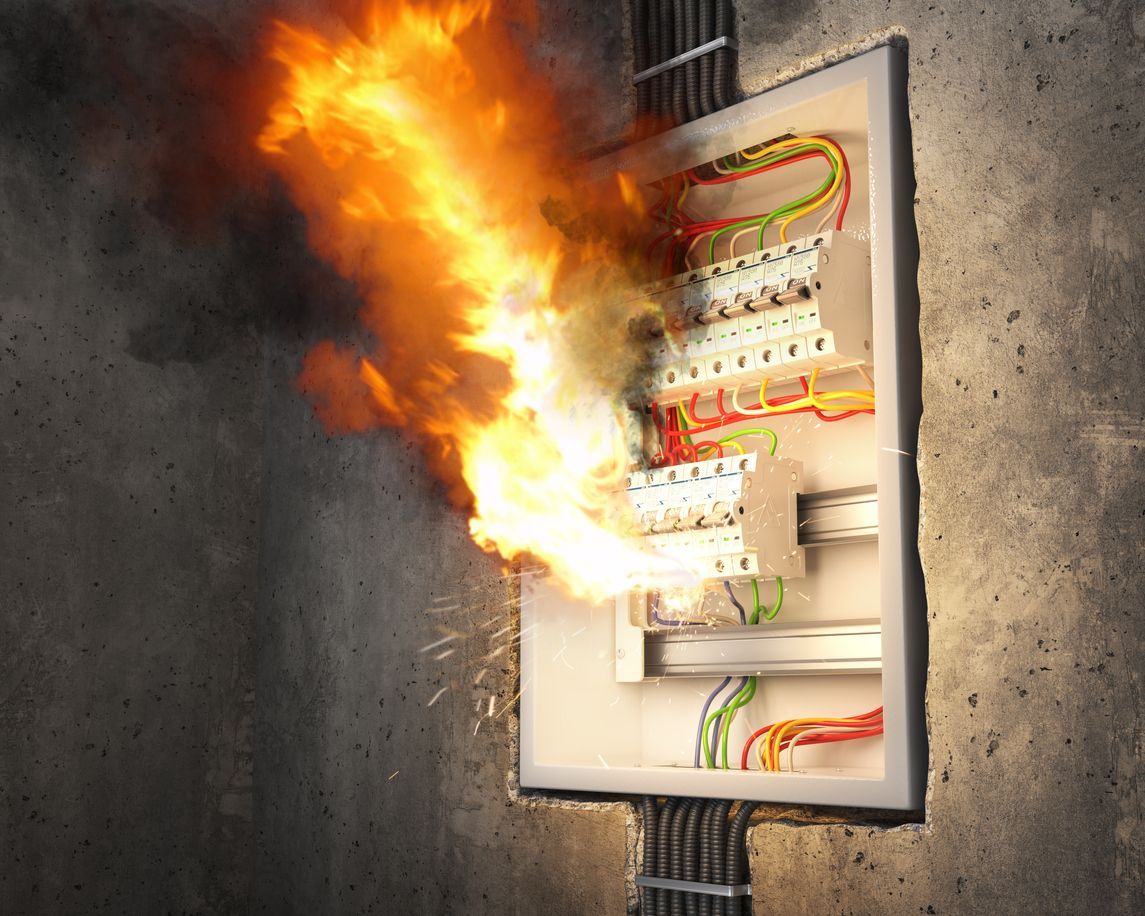
By Derek Jennings
•
February 7, 2025
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), in collaboration with the Partnership for Electrical Safety and KEMA Laboratories, has recently unveiled new guidance aimed at addressing arc flash hazards in the workplace. This guidance is a crucial update that highlights the need for comprehensive electrical safety programs that specifically include measures to protect against arc flash hazards. Here’s what employers need to understand about the new directives and how they can effectively respond. Understanding Arc Flash and OSHA's Recommendations An arc flash is a type of electrical explosion that results from a low-impedance connection to the ground or another voltage phase in an electrical system. The new guidance provided by OSHA not only offers a clear definition of what constitutes an arc flash but also elaborates on methods to mitigate such hazards during electrical work. The guidance includes detailed documents for employers and useful handouts for employees, emphasizing the common myths and the reality of arc flash dangers. The Role of NFPA 70E OSHA’s guidance strongly correlates with the standards outlined in NFPA 70E, the National Fire Protection Association’s standard for electrical safety in the workplace. Employers who are already compliant with NFPA 70E likely have a written Electrical Safety Program (ESP) that includes protocols for arc flash hazards. This new guidance serves to reinforce the importance of these existing standards while also urging those without comprehensive plans to take immediate action. What if You Don’t Have a Comprehensive ESP? For employers who have yet to develop an ESP that addresses arc flash hazards, OSHA’s guidance is a wake-up call. It is crucial to recognize that general workplace safety standards, although not specifying arc flash, require protection against electrical hazards under regulations like 1910.333. The absence of specific OSHA standards for arc flash does not excuse employers from the responsibility of protecting their employees from such risks. Implementing Effective Arc Flash Protection Measures Incident Energy Analysis: A foundational step in arc flash protection is conducting an incident energy analysis. This process involves studying the facility’s electrical systems to calculate the potential energy released in the event of an arc flash. Understanding this energy potential is essential for determining the arc flash boundary—the distance within which a person could receive second-degree burns or worse if exposed to an arc flash. Developing a Risk Assessment Procedure: Employ ers need to establish a procedure for assessing the risks associated with arc flash. This includes evaluating the tasks being performed, the condition of the electrical equipment, the maintenance history of the equipment, the energy involved, and the potentia l for human error. Deciding on Protective Measures: Once risks are assessed, decisions must be made regarding the best ways to protect employees. This often involves the use of Arc-Rated Pe rsonal Protective Equipment (PPE) and could also include engineering controls such as redesigning parts of the electrical system to minimize arc flash risks. Proactive Versus Reactive: The Choice is Yours The latest guidance from OSHA should be viewed as an unofficial yet critical call to action for employers to either update their existing safety measures or develop new protocols in line with NFPA 70E. Being proactive about electrical safety not only helps in compliance with OSHA’s standards but fundamentally enhances the safety and well-being of employees. Final Thoughts The introduction of OSHA’s arc flash guidance is a significant step toward heightened awareness and improved safety practices surrounding electrical hazards in the workplace. Employers are encouraged to review their current safety protocols, educate their workforce about the dangers of arc flash, and implement comprehensive measures to prevent such incidents. Always keep in mind that workplace safety begins with staying informed and well-prepared. Make it a habit to test before you touch it and prioritize safety like your life depended on it! For more insights into workplace safety and compliance, keep following our blog. Your safety is our priority, and together, we can foster a safer working environment for all. By Derek Jennings President SEA
10201 W. Markham Suite 317
Little Rock, Arkansas 72205
Phone: 888-374-3442
1750 Highway 160 West, Suite 101-147
Fort Mill, SC 29708
Phone: 839-400-2223
Our Hours
- Mon - Sun
- Open 24 Hours
© 2025
SEA Inc. | Powered by Flypaper | All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy

